Tutorial Setup
This tutorial focuses on GitHub users that are first-time Testspace users. It provides a reference project to walk-through to get new users up to speed on how Testspace works.
There are three steps required for setup:
- Install the Testspace App on your account
- Create a
testspace.getting-startedrepo on your GitHub account - Create a Testspace project associated with the repo
Install
The tutorial requires installing Testspace on your personal GitHub account or a GitHub organization account that you are an owner of:
Use the GitHub Marketplace to install Testspace - https://github.com/marketplace/testspace-com
Personal
The tutorial can be used with your personal GitHub account and a corresponding Testspace organization based on your "personal" account.
Personal Testspace accounts are always free.
Organization
Testspace can also be installed on a GitHub organization using the GitHub Marketplace. A new Testspace organization will be created that matches the name of your GitHub organization.
You must be an owner of the GitHub organization to install Testspace using the GitHub Marketplace.
Invite Others
When using a GitHub Organization account and a corresponding Testspace organization, it is easy to invite other GitHub members.
- At the Testspace Organization level, select the
Userstab. - Click the
Invite Usersbutton at the upper right of the page. - A list of all GitHub organization members will be presented.
- Select the members to invite and click on "SUMIT".
For more Testspace account admin information click here.
Tutorial Repo
The GitHub getting started repo includes (i) a CI workflow file used to publish automated test results and (ii) a set of Test Specs used for manual execution.
The repo can be forked or created.
If you fork, you are required to enable both Actions and Issues in the new repo.
Fork Repo
After forking the repo, make sure to go to your forked repo settings and add update the following:
- Enable Workflows. When a repository is forked, the GitHub Actions for automation has to be manually enabled.
- Enable Issues. Issues will be required to be
enabled, allowing Issues to be auto-generated by Testspace when a Manual test case fails.
Forked Repos require the settings to be updated.
Create Repo
To create your repo, based on testspace.getting-started repo, use the following instructions:
- Create an empty repo using the GitHub UI - assumed name
testspace.getting-started - Pull a copy of your newly created repo. Make sure to replace
USER-NAME.git init
git remote add origin https://github.com/USER-NAME/testspace.getting-started.git
git pull https://github.com/testspace-com/testspace.getting-started.git
git branch -M main
git push -u origin main
Tutorial Project
After the repo has been created and updated, login into your Testspace account. You will now create a Testspace project referencing the newly created GitHub repo.
To create a Testspace project click on the "New Project" button at the top right of the Testspace landing page. A dialog will appear listing all of the Repositories available. Select the name of the newly created GitHub repo (i.e. "testspace.getting-started") and press OK.
The your-github-org:testspace.getting-started project is now ready to be used for testing. The main space in the project is accessible by clicking the project that you created.
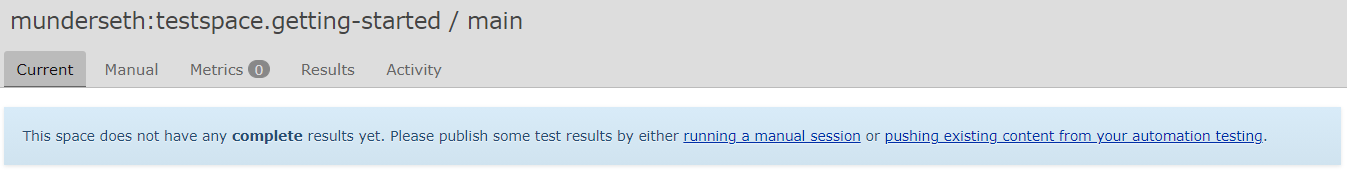
When clicking on the main space you should see empty results:
Terms
The following are some terms used throughout this tutorial.
space- Represents a branch in the repo.spec- A set of test instructions represented by a single markdown file. Aka test spec.suite- Contains testing status, made up of one or more test cases.
Recap
At this point, a new Testspace project has been created and connected to a new GitHub repo.
In this example, the Testspace project is used to manage results from test automation, manual test execution, and exploratory testing.
A Testspace project can be used for publishing test automation results, implementing and executing manual tests, and conducting exploratory testing.
Let's start doing things.